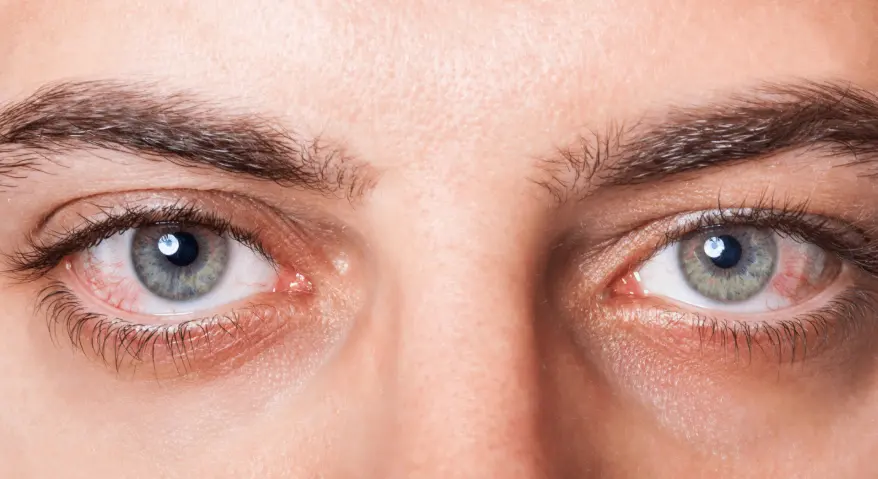
Red eyes are often not a single symptom; they are usually accompanied by irritation, burning, itching, or a feeling of something in the eye. Therefore, many people are eager to find effective relief when their eyes suddenly become red.
Generally speaking, most cases of red eye are mild and temporary, and can be improved with proper home care. However, some types of red eyes may indicate an underlying medical condition and require prompt medical attention.
To accurately choose the appropriate relief method, it is essential first to understand the causes of red eyes. This guide will systematically outline the common triggers of red eyes, at-home treatments, and warning signs that require immediate medical attention. Rest assured, we will help you step-by-step to better protect your eye health.
Common Causes of Red Eyes
Red eyes usually originate from the dilation and congestion of blood vessels in the conjunctiva or superficial layers of the eye. This inflammatory response is often caused by external stimuli or environmental factors. Common triggers include:
- Prolonged use of contact lenses or improper care
- Seasonal allergies (such as allergic conjunctivitis caused by pollen)
- Allergens such as pet dander, dust, and mold
- Dry or windy weather
- Chemical irritants such as cigarette smoke, perfume, and cologne
- Chlorine or other disinfectants in swimming pools
Besides external stimuli, certain lifestyle and physiological factors can also cause red eyes, such as insufficient sleep, alcohol consumption, digital eye strain from prolonged use of electronic devices, hormonal changes during pregnancy, certain systemic diseases, and side effects of certain eye drops or overuse of vasoconstrictor eye drops.
When Should You See a Doctor?
While many mild cases of red eye can resolve on their own with simple home care, you should consult an optometrist or ophthalmologist promptly if you experience any of the following to assess for more serious eye problems:
- Pain or soreness when moving your eyes
- Significant photophobia
- Accompanied by fever or general malaise
- Nausea or vomiting
- Increased discharge, pus, or crusting of the eyelashes
- Blurred vision, double vision, or decreased visual acuity
A variety of eye conditions can cause red eye, including conjunctivitis, uveitis, acute angle-closure glaucoma, blepharitis, and subconjunctival hemorrhage. Even without severe symptoms, if red eye persists for several days without improvement, it is recommended to have a professional examination as soon as possible to ensure that your eye health is not compromised.
How to Effectively Relieve Red Eye Symptoms
Many mild eye irritations can improve on their own with over-the-counter eye drops or simple home care. However, please remember: if red eye is accompanied by severe symptoms, or does not improve after several days, consult an ophthalmologist as soon as possible to rule out underlying eye diseases.
Professional Advice on Using Eye Drops
There are many types of eye drops on the market, and different ingredients have different functions. Choosing the wrong type may not only fail to relieve red eye but may even worsen the symptoms. Therefore, it is essential to understand the purpose and precautions of each type of drop before using them.
1. Lubricating Eye Drops (Artificial Tears)
Lubricating eye drops are the most common and safest choice for relieving redness and dryness. They mimic natural tears, increasing the moisture content of the eye surface.
Suitable for: Red eye caused by dryness, mild irritation, or environmental factors.
Professional Advice: Prioritize preservative-free formulas, which are more suitable for long-term or frequent use.
2. Anti-allergy Eye Drops
For red eyes caused by allergens such as pollen, dust, pet dander, and mold, choose anti-allergy drops containing antihistamines or mast cell stabilizers.
Pre-use tip: It is best to consult an ophthalmologist or allergist first and strictly follow the instructions.
3. Decongestant "Redness-Reducing" Eye Drops
These drops work by constricting blood vessels on the surface of the eye, providing temporary relief from redness.
Risk warning: Long-term or frequent use may cause "rebound congestion," making the eyes redder than before. Use only when necessary for a short period, and consult a doctor before repeated use.
Natural Relief Methods Without Eye Drops
If you wish to try natural methods to relieve red eyes, you can refer to the following measures. However, please note: if symptoms persist, you should still consult a doctor to determine the cause.
1. Cold and Warm Compresses
Both cold and warm compresses can help reduce inflammation or relieve discomfort. Choose the method that suits you best based on your personal preference.
- Warm Compress: Apply a warm (not hot) damp towel to your closed eyes for 10 minutes to promote tear production and relieve dryness.
- Cold Compress: Use a towel soaked in cold water or chilled cucumber slices to reduce redness and itching.
A dedicated eye mask that can be heated or cooled is a more stable and reusable option.
2. Cleaning Eyelids and Eyelashes
- Gentle cleaning helps remove oil, secretions, and possible irritants.
- You can gently wipe your closed eyes with warm water and a clean towel, or rinse the surface of your eyes with saline solution for a safe and effective solution.
3. Avoid Allergens and Irritants
- For those with known allergies, reducing exposure to allergens such as pollen, dust, pet dander, and mold is essential.
- Other common irritants such as cigarette smoke, chlorine, and strong perfumes should also be avoided as much as possible.
- If you are unsure whether you have allergies, schedule an appointment with an allergist for testing.
4. Improve Indoor Air Quality
- If mold is a trigger, clean your ventilation system, replace your air filter, and use a dehumidifier.
- If dryness is causing discomfort, use a humidifier to improve air humidity.
- Avoid sitting directly in front of a fan or air conditioner vent for extended periods, as this can worsen dry eyes or expose your eyes to frequent allergen exposure.
5. Reduce Screen Time
Prolonged screen time can cause eye strain and redness. Try the following:
- Blink regularly
- Reduce screen brightness
- Adjust your work distance
- Follow the "20-20-20" rule: Every 20 minutes, look at something 20 feet (about 6 meters) away for at least 20 seconds.
Hopefully, this guide to red eye will provide you with practical and reliable information. Whether you choose to relieve discomfort through eye drops, hot or cold compresses, or other home care methods, you should closely monitor changes in your symptoms. If red eye persists for several days without improvement, or is accompanied by pain, changes in vision, increased discharge, or other abnormalities, be sure to consult an ophthalmologist promptly to ensure there are no underlying eye conditions that may be overlooked.